Let's talk: +91 79743 29894
Let's talk: +91 79743 29894
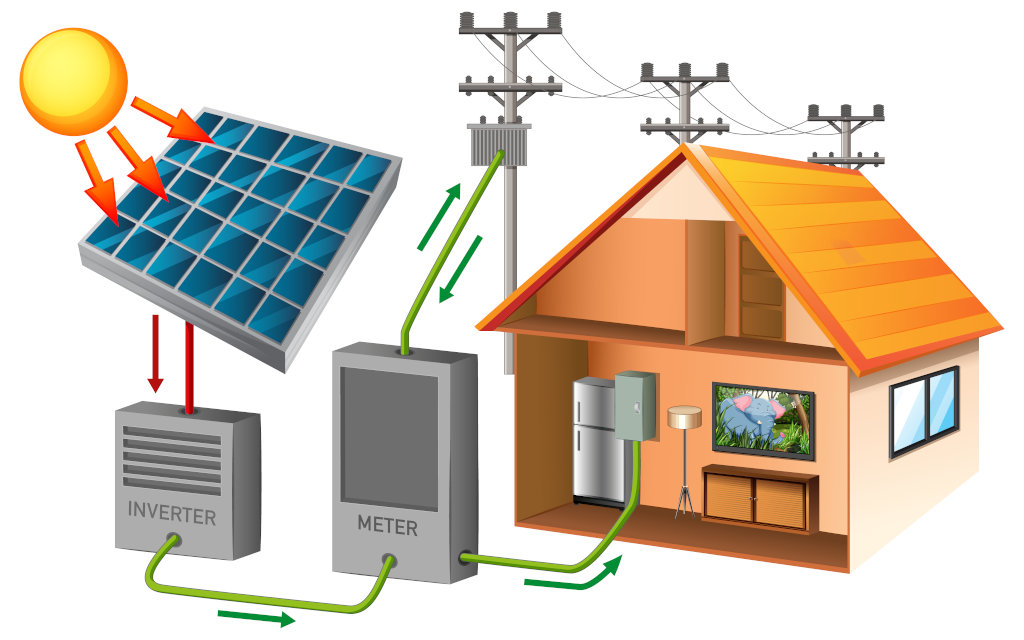
An on-grid solar power system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected solar power system, is a renewable energy system that generates electricity from solar panels and is connected to the utility grid. It allows users to both consume electricity from the grid and sell excess electricity back to the grid. If the solar panels produce more electricity than the building's demand, the excess energy is sent back to the grid through the bi-directional meter. When the solar panels are not generating enough electricity (e.g., at night or during cloudy periods), the building draws electricity from the grid. The bi-directional meter measures the net energy consumption or generation, and the user is billed accordingly or credited for the surplus electricity sent back to the grid.
Components of an on-grid solar power system:
Here are some major advantages of an On-Grid Solar Power System:
It's important to note that on-grid solar power systems do not provide backup power during grid outages. For uninterrupted power supply, additional equipment such as battery storage or backup generators can be added to the system. Consulting with a professional solar installer or engineer is recommended for designing and installing an on-grid solar power system that meets local regulations and requirements.